Solar Power That Never Fails: Building Resilient Energy Systems for Europe

Power system resilience stands at the forefront of Europe’s energy transformation, where grid stability meets the growing demands of renewable integration. As climate-related disruptions and cyber threats intensify, robust power systems must adapt to maintain continuous operations under increasingly challenging conditions. Modern power networks face unprecedented challenges: integrating variable renewable sources, managing bidirectional power flows, and protecting critical infrastructure against both physical and digital threats.
The evolution of power system resilience transcends traditional reliability metrics, encompassing adaptive capacity, rapid recovery capabilities, and proactive risk management. European utilities and energy providers are pioneering innovative approaches that combine advanced monitoring systems, smart grid technologies, and distributed energy resources to create more resilient power networks. These solutions not only protect against disruptions but also enable swift recovery when incidents occur.
For business leaders and technical decision-makers, understanding power system resilience is no longer optional—it’s fundamental to ensuring operational continuity and sustainable growth. The integration of resilience strategies with renewable energy systems, particularly solar installations, creates a robust framework that supports both environmental goals and business reliability requirements. This comprehensive approach to power system resilience delivers tangible benefits: reduced downtime, enhanced grid stability, and improved return on energy investments.
Why Power System Resilience Matters in Solar Energy
Key Challenges to Solar Power Stability
While solar power systems offer remarkable sustainability benefits, several solar energy reliability challenges need careful consideration. Weather variability remains a primary concern, with cloud cover, heavy rainfall, and seasonal changes affecting power generation predictability. European regions particularly face distinct challenges due to varying daylight hours between seasons and frequent overcast conditions.
Grid integration poses another significant challenge, as sudden fluctuations in solar power output can stress existing infrastructure. This intermittency requires sophisticated power management systems and often backup solutions to maintain stable energy supply. Temperature fluctuations also impact panel efficiency, with both extreme heat and cold potentially reducing system performance.
Physical threats such as storm damage, hail, and snow accumulation can compromise system integrity, while dust and debris accumulation gradually decrease panel efficiency if not properly maintained. Additionally, aging infrastructure and component degradation over time necessitate regular monitoring and maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for implementing robust solar solutions that deliver reliable, long-term energy security for European homes and businesses.
The Cost of Power System Failures
Power system failures can have far-reaching financial implications for both businesses and households across Europe. Recent studies indicate that unplanned solar system downtime costs European businesses an average of €5,000 to €50,000 per day, depending on the organisation’s size and energy requirements. For manufacturing facilities, these costs can escalate significantly due to production losses, spoiled materials, and missed delivery deadlines.
Beyond immediate financial losses, power system failures impact operational continuity and customer trust. Companies investing in business energy resilience strategies typically see 60% lower downtime-related costs compared to unprepared counterparts. For households, system failures can lead to unexpected expenses, comfort disruptions, and potential damage to sensitive electronic equipment.
The indirect costs are equally significant: decreased productivity, data loss, security system vulnerabilities, and potential regulatory compliance issues. These challenges underscore the importance of implementing robust backup systems and preventive maintenance protocols. Investment in system resilience, while requiring initial capital, typically delivers a return on investment within 2-3 years through avoided downtime costs and enhanced operational reliability.
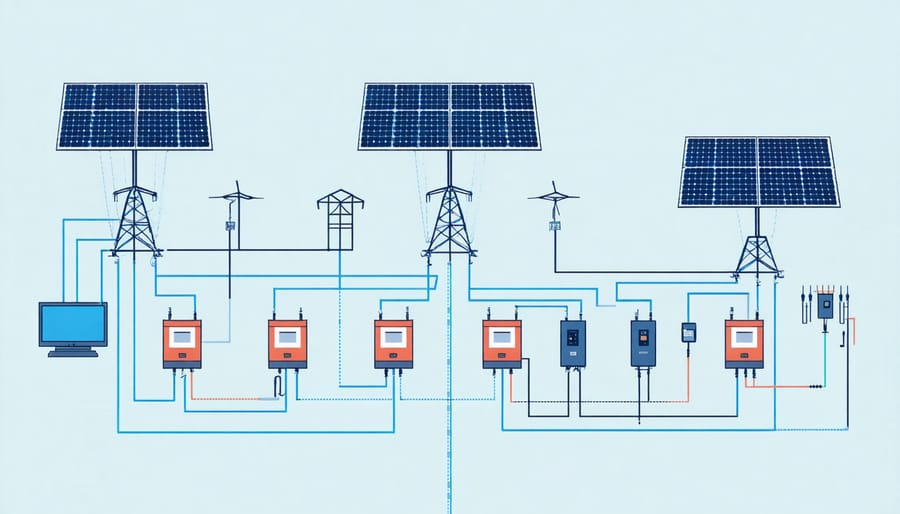
Core Technologies for Solar Energy Resilience
Advanced Battery Storage Solutions
Advanced battery storage systems have revolutionized power system resilience by providing crucial backup power and grid stabilization capabilities. Modern lithium-ion batteries, along with emerging technologies like flow batteries and solid-state systems, offer increasingly sophisticated solutions for both residential and commercial applications.
These storage solutions serve multiple functions in enhancing system resilience. During peak demand periods, they can discharge stored energy to reduce grid strain and prevent power fluctuations. In the event of grid failures, they provide seamless power transition, ensuring critical operations continue uninterrupted. This capability is particularly valuable for European businesses where power continuity is essential for maintaining operations and protecting sensitive equipment.
The integration of smart battery management systems (BMS) has significantly improved storage efficiency and longevity. These systems continuously monitor battery health, optimize charging cycles, and adjust performance based on real-time demand patterns. Modern storage solutions also feature advanced thermal management and safety protocols, addressing previous concerns about battery stability and maintenance.
For European property owners, battery storage systems are increasingly becoming a standard component of renewable energy installations. They not only enhance system resilience but also enable greater energy independence and cost optimization through strategic energy management. The latest storage solutions can be scaled according to specific needs, from compact residential units to large-scale industrial applications, making them a versatile investment in power system reliability.

Smart Grid Integration Systems
Smart grid integration systems represent a crucial advancement in enhancing power system resilience through intelligent networking and automated management capabilities. These systems combine advanced sensors, communication technologies, and sophisticated control algorithms to create a more responsive and adaptive power infrastructure.
At the heart of this integration is the seamless coordination between traditional power sources and renewable energy installations. Modern smart grid systems enhance solar power system stability through real-time monitoring and automated response mechanisms. When fluctuations occur, these systems can instantly adjust power flow, maintaining grid stability and preventing potential disruptions.
European grid operators are implementing innovative features such as self-healing capabilities, which automatically detect, isolate, and resolve power distribution issues. This technology significantly reduces downtime and improves overall system reliability. Advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) provides detailed consumption data, enabling better load management and more efficient energy distribution.
The integration also supports bi-directional power flow, essential for properties with solar installations that both consume and generate electricity. Smart inverters work in conjunction with these systems to maintain optimal voltage levels and power quality, while automated switching systems ensure seamless transitions between different power sources.
For businesses and homeowners, these innovations translate into more reliable power supply, reduced energy costs, and improved integration of renewable energy sources into the existing grid infrastructure.
Monitoring and Control Technologies
Modern power systems rely heavily on sophisticated monitoring and control technologies to maintain resilience and optimal performance. Advanced SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems form the backbone of these monitoring solutions, providing real-time insights into system operations and potential issues.
Smart sensors distributed throughout the power network continuously collect data on voltage levels, power quality, equipment temperature, and weather conditions. This information feeds into intelligent monitoring platforms that use artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyse patterns and predict potential system vulnerabilities.
Digital twin technology has emerged as a powerful tool for system operators, creating virtual replicas of physical power infrastructure that enable sophisticated simulation and testing scenarios. These digital models help operators optimize system performance and prepare for various contingencies without risking actual infrastructure.
Remote monitoring capabilities allow system operators to track performance metrics and respond to issues from centralised control rooms. Advanced automation systems can implement immediate corrective actions when anomalies are detected, often resolving potential problems before they impact service delivery.
Integration with weather forecasting systems particularly benefits renewable energy installations, enabling proactive adjustments to maintain grid stability during varying weather conditions. Modern monitoring platforms also incorporate cybersecurity features to protect against digital threats, ensuring both physical and digital resilience of power systems.
Implementation Strategies for Maximum Resilience
System Design Considerations
When planning a resilient solar installation, several critical design considerations must be addressed from the outset. The system’s physical location plays a crucial role, with factors such as wind exposure, snow loads, and local climate patterns influencing the structural requirements. In Europe, where weather patterns can vary significantly by region, installations must comply with EN 1991 Eurocode standards for structural safety.
Component selection forms another vital aspect of system resilience. High-quality inverters with advanced grid-support features, robust mounting systems, and premium solar panels with proven durability ratings contribute to long-term system reliability. Modern installations increasingly incorporate smart monitoring systems that enable real-time performance tracking and early problem detection.
Redundancy in critical components adds another layer of resilience. This might include multiple inverter configurations, backup power systems, and strategic array segmentation to prevent total system failure. Energy storage integration has become increasingly important, with battery systems providing both backup capability and grid stabilization benefits.
The electrical design must account for potential grid disturbances, incorporating appropriate surge protection devices and isolation mechanisms. Additionally, smart grid compatibility ensures the system can respond effectively to grid signals while maintaining stable operation during network fluctuations.
Maintenance accessibility should be considered during the design phase, with adequate spacing between components and clear access routes for service personnel. This forward-thinking approach significantly reduces system downtime during routine maintenance or repairs.
Maintenance and Upgrade Protocols
Regular maintenance and strategic upgrades are essential pillars of power system resilience. For optimal performance, implement a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes quarterly inspections of all system components, with particular attention to inverter functionality and cable connections. These routine checks should be documented in a maintenance log, enabling better tracking of system performance and early detection of potential issues.
Upgrade protocols should follow a systematic approach, beginning with annual assessments of system efficiency against current technological standards. When planning upgrades, prioritise components that directly impact system reliability, such as smart monitoring systems and advanced battery storage solutions. European standards require that all modifications comply with the latest grid codes and safety regulations.
For enhanced resilience, implement predictive maintenance strategies using data analytics and remote monitoring systems. These tools can identify performance trends and flag potential failures before they occur, significantly reducing system downtime. Consider integrating weather forecasting data to optimise system performance during varying environmental conditions.
Establish clear procedures for emergency responses and backup operations. This includes maintaining an inventory of critical spare parts and establishing relationships with qualified service providers. For businesses and industrial installations, develop a detailed contingency plan that outlines steps for maintaining essential operations during system maintenance or upgrades.
Regular staff training on system operations and basic troubleshooting procedures further strengthens overall system resilience, ensuring quick response times during technical issues.
Future-Proofing Your Solar Investment
As the solar energy landscape continues to evolve, implementing effective long-term energy resilience strategies becomes crucial for maximising your investment. Today’s forward-thinking approach combines cutting-edge technology with adaptable infrastructure to ensure your solar system remains efficient and reliable for decades to come.
Smart inverter technology represents one of the most significant advances in future-proofing solar installations. These sophisticated devices not only convert solar power more efficiently but also provide enhanced grid support capabilities and remote monitoring options. By choosing inverters with firmware update capabilities, you can adapt to new grid requirements and energy management protocols without hardware replacement.
Energy storage integration is another key consideration. Modern battery systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering improved capacity and longer lifespans. When designing your solar installation, consider leaving space for future battery integration or expansion, even if you’re not ready to implement storage immediately.
Digital monitoring and predictive maintenance systems are revolutionising how we manage solar installations. These platforms use artificial intelligence to detect potential issues before they become problems, optimising performance and extending system life. Investing in comprehensive monitoring solutions helps ensure your system operates at peak efficiency while minimising unexpected downtime.
Infrastructure readiness is equally important. Ensure your mounting systems and electrical infrastructure can accommodate future panel upgrades and additional capacity. This might include oversizing conduits, installing extra junction boxes, or choosing mounting systems with modular expansion capabilities.
Consider also the emerging trend of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) integration. As electric vehicles become more prevalent, the ability to integrate your solar system with V2G technology could provide additional flexibility and value. Planning for this integration now can save significant costs in the future.
Regular consultation with solar professionals who stay current with industry developments can help you adapt your system as technology evolves. This proactive approach ensures your investment continues to deliver optimal returns while maintaining resilience against future challenges.
Building a resilient solar power system requires careful planning, strategic implementation, and ongoing maintenance. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components and strategies that contribute to system resilience, from robust equipment selection to advanced monitoring solutions. The key to success lies in adopting a comprehensive approach that addresses both technical and operational aspects of your solar installation.
To implement a truly resilient solar power system, consider starting with a thorough site assessment and risk analysis. This foundation will guide your decisions on equipment selection, system architecture, and backup solutions. Invest in high-quality components that meet European standards and work with certified installers who understand local requirements and conditions.
Remember that resilience is an ongoing process, not a one-time achievement. Regular maintenance, system monitoring, and periodic assessments are crucial for maintaining optimal performance. Consider implementing smart monitoring systems that provide real-time data and predictive maintenance capabilities to prevent potential issues before they arise.
For European property owners and businesses, the path to power system resilience also means staying informed about evolving technologies and regulations. Engage with renewable energy communities, participate in knowledge-sharing networks, and maintain open communication with your system providers and maintenance teams.
By following these guidelines and maintaining a proactive approach to system management, you can ensure your solar installation remains reliable, efficient, and capable of meeting your energy needs for years to come.
Leave a Reply