Solar Backup Power That Keeps Your Home Running When Grid Power Fails

Power outages disrupt modern life in ways our grandparents never imagined – from frozen food spoilage to dead security systems and non-functioning medical equipment. As extreme weather events become more frequent across Europe, home backup power systems have evolved from luxury to necessity. Today’s integrated power solutions combine solar panels, battery storage, and smart controllers to create resilient home energy systems that work seamlessly during grid failures.
Modern backup power systems do more than just keep the lights on. They protect valuable appliances, maintain critical medical devices, and ensure business continuity for remote workers. With advancing battery technology and decreasing solar costs, European homeowners can now design backup systems that provide days of autonomous power while contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
The key lies in choosing the right combination of components – from hybrid inverters that manage multiple power sources to lithium battery banks that store excess solar energy. Whether you’re protecting against brief power cuts or preparing for extended outages, today’s backup solutions can be precisely tailored to your home’s unique energy needs and usage patterns.
Why Solar Backup Power Makes Sense for European Homes
Energy Independence and Grid Resilience
Modern hybrid solar systems are revolutionising how European homeowners achieve energy independence. By combining solar panels with advanced battery storage technology, these systems provide reliable backup power during grid outages while contributing to daily energy needs. This dual functionality ensures homes remain powered during blackouts and reduces dependency on conventional grid electricity.
The resilience offered by solar backup systems extends beyond individual households to strengthen local grid stability. When numerous homes in a neighbourhood maintain their own power reserves, it reduces strain on the main grid during peak demand periods. This distributed energy approach aligns with EU initiatives for grid modernisation and climate resilience.
For homeowners, the ability to generate and store their own clean energy represents a significant step toward energy autonomy. During daylight hours, excess solar energy charges the battery system, creating a reliable power reserve for evenings or emergencies. This self-sufficiency becomes particularly valuable during extreme weather events or grid maintenance, ensuring essential appliances and systems remain operational when traditional power sources fail.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Investing in a backup power system for your home delivers substantial environmental and economic advantages. Modern backup solutions, particularly those integrated with solar energy systems, significantly reduce your carbon footprint by decreasing reliance on fossil fuel-based grid power. When combined with renewable energy sources, these systems can lower household CO2 emissions by up to 80% compared to traditional power sources.
From an economic perspective, backup power systems offer impressive long-term savings. While the initial investment may seem substantial, homeowners typically recover costs through reduced energy bills within 5-7 years. During peak demand periods, when grid electricity prices surge, your backup system can provide power at a fraction of the cost. Additionally, many European countries offer attractive incentives and tax benefits for installing sustainable backup power solutions.
These systems also protect against rising energy costs and potential grid price fluctuations. By generating and storing your own power, you gain greater control over your energy expenses while contributing to a more sustainable future. The increased property value associated with having a reliable backup power system further enhances the economic benefits of this investment.
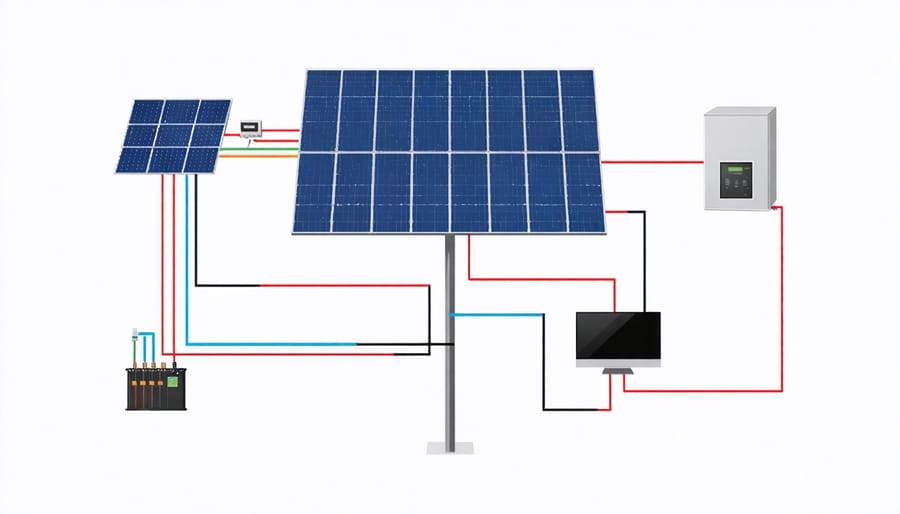
Essential Components of a Solar Backup System
Solar Panels and Power Generation
Solar panels form the cornerstone of modern backup power systems, converting sunlight into reliable electricity for your home. Monocrystalline panels, known for their high efficiency and compact design, are particularly well-suited for European climates. These panels typically offer conversion rates between 15-22%, making them an excellent choice for residential installations.
For backup systems, panels rated between 350-400 watts are most common, with premium models reaching up to 500 watts per panel. When selecting panels, consider both their peak power output and their performance in low-light conditions, which is especially important in Northern European regions.
Key specifications to evaluate include temperature coefficient (ideally -0.35%/°C or better), warranty duration (typically 25 years for performance), and certification standards (look for IEC 61215 and IEC 61730). Most residential backup systems require 6-12 panels, depending on household consumption and available roof space.
Bifacial panels, which can capture reflected light from both sides, are gaining popularity in backup installations, offering up to 30% additional energy yield in optimal conditions. These innovative panels work particularly well with light-colored surfaces or in snow-prone areas.
Battery Storage Solutions
Modern battery storage solutions offer homeowners reliable ways to store excess energy for backup power needs. The most common technology for residential applications is lithium-ion batteries, praised for their efficiency, long lifespan, and decreasing battery storage costs. These systems typically range from 5kWh to 15kWh for average European homes, with the possibility to stack multiple units for increased capacity.
Advanced lead-acid batteries remain a cost-effective option, particularly for smaller backup systems, though they require more maintenance and have shorter lifespans than their lithium counterparts. The newest generation of saltwater batteries presents an environmentally friendly alternative, using non-toxic materials and offering excellent safety features, albeit at a higher initial investment.
When selecting a battery system, homeowners should consider several key factors: daily energy consumption, critical loads during outages, desired backup duration, and available installation space. Most modern systems include smart energy management features that optimize charging cycles and protect battery health.
For maximum efficiency, battery storage systems can be integrated with solar panels and smart home technologies. This integration allows for automated switching between power sources and remote monitoring through mobile applications, providing peace of mind and enhanced energy independence for European households.

Inverters and Control Systems
Modern inverters serve as the intelligence hub of home backup power systems, converting stored DC power into usable AC electricity while maintaining optimal system performance. These sophisticated devices work seamlessly with energy management systems to monitor power flow, adjust charging patterns, and ensure seamless switching between grid and backup power.
Today’s smart inverters offer remote monitoring capabilities through mobile apps, allowing homeowners to track system performance, energy consumption, and battery status in real-time. They incorporate advanced features like grid stabilization, power factor correction, and adaptive charging algorithms to maximize system efficiency and battery lifespan.
For European households, hybrid inverters are particularly valuable as they can manage multiple power sources simultaneously, including solar panels, batteries, and grid power. These systems automatically prioritize self-consumption of solar energy, only drawing from the grid when necessary, and ensure uninterrupted power supply during outages.
The integration of smart technology also enables predictive maintenance, automatic system updates, and optimization based on usage patterns, making these systems increasingly reliable and user-friendly.
Sizing Your Solar Backup System
Calculating Power Requirements
To accurately determine your backup power needs, start by conducting a comprehensive energy audit of your home. Begin by listing all essential appliances and devices you’ll need during a power outage. For each item, locate the power rating (usually in watts) on the device label or manual, then multiply this by the number of hours you expect to use it daily.
Key appliances typically include refrigerators (150-400W), lighting (5-60W per bulb), heating systems (1000-3000W), and essential medical equipment if applicable. Remember that some devices, particularly those with motors, require additional startup power – sometimes 2-3 times their running wattage.
When designing your solar system, calculate both your continuous power requirements and peak loads. Add up the wattage of devices that run simultaneously and include a 20% safety margin to account for unforeseen needs and system inefficiencies.
For European homes, seasonal variations significantly impact power requirements. Winter months may demand more energy for heating and lighting, while summer might require additional cooling power. Consider creating a seasonal usage chart to ensure your backup system remains effective year-round.
A typical European household might need anywhere from 5 to 15 kWh of daily backup capacity, depending on size and usage patterns. Document your calculations carefully, as they’ll form the foundation of your backup power system specifications.

System Scaling and Future-Proofing
When planning a backup power system for your home, considering future expansion and technological advancements is crucial for long-term value. Modern backup systems are designed with modularity in mind, allowing homeowners to start with essential coverage and scale up as needs change or budget allows.
To future-proof your installation, begin by assessing potential future power requirements. Consider upcoming home additions, electric vehicle charging needs, or the possibility of integrating smart home technologies. Choose inverters and control systems that offer expandable capacity and compatibility with various energy storage solutions.
The rapid advancement of battery technology presents exciting opportunities. While current lithium-ion systems offer excellent performance, emerging technologies like solid-state batteries promise even greater efficiency and longevity. Selecting systems with flexible battery integration capabilities ensures you can upgrade to newer storage technologies as they become available.
Smart monitoring and management systems play a vital role in scalability. Modern systems feature cloud connectivity and sophisticated software that can be updated remotely, ensuring your installation remains current with the latest energy management innovations.
When discussing system specifications with installers, request documentation about expansion capabilities and upgrade paths. European regulations increasingly support renewable energy integration, making it essential to choose systems that comply with current standards while maintaining flexibility for future grid requirements and energy sharing initiatives.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Professional Installation Requirements
In Europe, the installation of backup power systems must comply with strict regulations and safety standards. Professional installation is not just recommended—it’s mandatory under EU directives and national regulations. Installers must hold relevant certifications, including the European Installation Qualification (EIQ) for energy storage systems and specific national certifications that vary by country.
Key certification requirements include expertise in electrical systems (EN 50438), energy storage installation (IEC 62619), and adherence to grid connection standards. Installers must also demonstrate competency in working with renewable energy systems, particularly when integrating solar solutions with backup power systems.
For safety compliance, installations must meet the Low Voltage Directive (LVD) 2014/35/EU and Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive 2014/30/EU. These regulations ensure system safety and optimal performance while maintaining grid stability. Additionally, installers need to be familiar with local building codes and obtain necessary permits before beginning installation work.
Documentation requirements include detailed system specifications, safety protocols, and maintenance schedules. Professional installers must provide comprehensive handover documentation, including warranty information and emergency procedures. Regular system inspections and maintenance must be performed by certified professionals to maintain warranty validity and ensure continued compliance with safety standards.
To protect homeowners’ investments and ensure system reliability, it’s essential to work only with certified installation professionals who can demonstrate compliance with these European standards and regulations.
Maintenance and System Monitoring
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring your backup power system remains reliable when you need it most. For battery-based systems, quarterly inspections should include checking connection tightness, cleaning terminals, and monitoring electrolyte levels in traditional lead-acid batteries. Modern lithium-ion systems require less frequent maintenance but should still undergo annual professional inspections.
Implement a monthly testing schedule for your entire backup system. This involves running the system for a short period to verify all components are functioning correctly. During these tests, pay attention to any unusual sounds, vibrations, or performance issues that might indicate potential problems.
Smart monitoring solutions have revolutionised system maintenance by providing real-time performance data and early warning signals. Many modern systems come with mobile apps that track battery health, power flow, and system efficiency. These tools can alert you to potential issues before they become critical problems.
Keep detailed maintenance records, including dates of inspections, test results, and any repairs or replacements. This documentation helps track system performance over time and can be valuable for warranty claims or troubleshooting.
For optimal performance, schedule professional maintenance annually. Qualified technicians can perform comprehensive system checks, calibrate equipment, and identify components that may need replacement. This proactive approach helps prevent unexpected failures and extends the system’s lifespan.
The implementation of a solar backup power system represents a significant step toward energy independence and sustainability for European homeowners. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the essential components, from battery storage solutions to inverters, and the critical considerations for system sizing and installation. These systems not only provide peace of mind during power outages but also contribute to reduced energy costs and a smaller carbon footprint.
As energy security becomes increasingly important across Europe, investing in a solar backup power system is more relevant than ever. The combination of advancing technology, decreasing installation costs, and generous government incentives makes this an opportune time to take action. Remember that proper planning, professional installation, and regular maintenance are key to maximizing your system’s efficiency and longevity.
To begin your journey toward energy independence, consider conducting an energy audit of your home and consulting with certified solar installers who understand local regulations and requirements. Take advantage of available resources, including energy efficiency calculators and regional solar mapping tools, to optimize your system design.
The transition to solar backup power is not just about emergency preparedness; it’s an investment in your property’s value and our planet’s future. By taking this step, you join a growing community of European homeowners leading the charge toward a more sustainable and resilient energy landscape.
Leave a Reply