Series-Connected Solar Panels: Powering Your Building’s Future

Connecting four solar panels in series multiplies voltage output while maintaining consistent current flow, creating an efficient power generation system for residential and commercial buildings across Europe. This configuration transforms standard 24V panels into a robust 96V array, delivering the higher voltage requirements modern grid-tie inverters demand. Professional installers routinely choose series connections to minimize power losses in longer cable runs and optimize energy harvesting during varying light conditions. Whether retrofitting an existing structure or planning a new installation, understanding the precise mechanics of series connections ensures maximum system performance while adhering to EU safety standards and local building codes. The strategic placement of four panels in series has become a cornerstone configuration in sustainable building design, offering an ideal balance between power output and installation complexity for property owners seeking energy independence.
Understanding Series Connection in Solar Arrays
Basic Principles of Series Connection
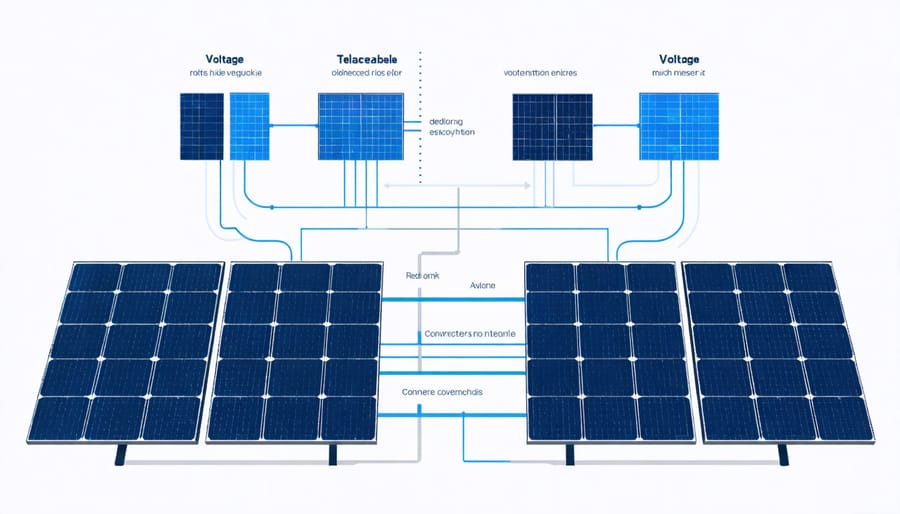
When connecting solar panels in series, the fundamental principle is that voltages add up while the current remains constant throughout the circuit. In a series connection, the positive terminal of one panel connects to the negative terminal of the next panel, creating a single path for electrical flow. This configuration is similar to connecting batteries in series.
For example, if each solar panel produces 24 volts, four panels connected in series will generate a total of 96 volts. However, the current (measured in amperes) stays the same as what a single panel produces, typically around 8-10 amperes in standard residential panels.
This voltage addition makes series connections particularly useful for systems requiring higher voltages to operate efficiently, such as grid-tied inverters commonly used in European installations. The higher voltage also helps reduce power losses in the cables, especially when panels are installed at considerable distances from the inverter.
Understanding these principles is crucial for proper system design and ensuring optimal energy harvest from your solar installation.
Advantages of 4-Panel Series Configuration
Connecting four solar panels in series offers several significant advantages for building integration projects. The most notable benefit is the increased voltage output, which allows for more efficient power transmission over longer distances with reduced cable losses. This configuration is particularly valuable for European installations where roof space might be limited but higher voltage requirements need to be met.
The series arrangement simplifies the overall system design by reducing the number of required components. With four panels in series, you’ll need fewer string inverters and combiner boxes, leading to lower installation costs and reduced maintenance requirements. This streamlined setup also minimizes potential points of failure in the system.
Another key advantage is the enhanced flexibility in system design. The higher voltage output from a four-panel series configuration enables better compatibility with modern grid-tie inverters, making it easier to meet local electrical codes and standards. This arrangement also provides optimal performance during partial shading conditions when combined with power optimizers, ensuring maximum energy yield throughout the day.
For building-integrated installations, the series configuration helps maintain consistent electrical characteristics across the array, resulting in more stable and predictable system performance.
Integration with Building Materials
Roofing Integration Solutions
Modern building-integrated solar solutions have revolutionized how we incorporate series-connected solar panels into roofing systems. For a four-panel series configuration, several integration methods have proven particularly effective across European installations.
The most common approach involves using specialized mounting rails that align with existing roof tiles or slates. These rails create a waterproof channel system that accommodates the series wiring while maintaining the roof’s integrity. For new constructions, in-roof mounting systems allow panels to sit flush with the roof surface, replacing traditional roofing materials entirely in the installed area.
Solar tiles and integrated panels offer another elegant solution, especially for heritage buildings or areas with strict aesthetic requirements. These systems incorporate series connections within specially designed roof elements, concealing all wiring and junction boxes beneath the surface.
For flat roofs, ballasted mounting systems provide an excellent integration option. These systems use weighted frames that maintain panel positioning without penetrating the roof membrane, while cable channels protect the series connections from environmental exposure.
Installation considerations should include proper water drainage paths between panels, thermal expansion gaps, and accessible routes for maintenance. Additionally, ensuring adequate ventilation beneath the panels helps maintain optimal operating temperatures and system efficiency.

Façade Implementation
Vertical installation of four solar panels in series requires careful consideration of building aesthetics and structural integrity. Modern building-integrated photovoltaic systems offer seamless integration options that transform façades into power-generating surfaces while maintaining architectural appeal.
For optimal façade implementation, mounting rails must be securely anchored to the building structure, typically using specialized brackets that accommodate both the weight of the panels and wind loads. The series connection should be arranged to minimize visible wiring, with cables concealed within dedicated channels or building cavities.
Temperature management becomes particularly crucial in vertical installations, as façade-mounted panels typically experience higher operating temperatures than roof installations. Maintaining adequate air circulation behind the panels through properly designed ventilation gaps (typically 5-10cm) helps prevent performance degradation and extends system longevity.
When integrating series-connected panels into building faces, consider:
– Solar orientation and shading patterns from surrounding structures
– Local building codes and safety regulations
– Weather-sealing requirements at mounting points
– Access provisions for maintenance
– Lightning protection integration
– Aesthetic uniformity with existing façade elements
Modern mounting systems often incorporate adjustable components to ensure precise panel alignment, creating a professional finish that complements the building’s architecture while maximizing energy generation potential.
Installation and Performance Optimization
Wiring and Connection Guidelines
When connecting four solar panels in series, proper wiring techniques are essential for optimal performance and safety. Begin by identifying the positive (+) and negative (-) terminals on each panel, typically marked clearly on the junction boxes. Use appropriate MC4 connectors and solar-rated cables with minimum 4mm² cross-sectional area to ensure efficient power transmission.
Connect the panels sequentially by linking the positive terminal of the first panel to the negative terminal of the second panel, continuing this pattern until all four panels are connected. The system’s main output will be from the positive terminal of the first panel and the negative terminal of the fourth panel.
Ensure all connections are weather-sealed and properly insulated. Use UV-resistant cable ties to secure wiring against wind and weather exposure. Maintain appropriate cable spacing and avoid sharp bends that could damage the insulation. Install blocking diodes to prevent reverse current flow during low-light conditions.
For maximum safety, incorporate proper grounding connections and surge protection devices. Keep cable runs as short as possible to minimise voltage drops. When routing cables, maintain a minimum bend radius of 4-5 times the cable diameter and use appropriate conduit protection where necessary.
Remember to verify polarity before making final connections and test the total voltage output, which should equal the sum of individual panel voltages. Document all connections for future maintenance reference.

Performance Monitoring Systems
Effective solar performance monitoring is crucial for maintaining optimal energy production in series-connected solar panels. Modern monitoring systems typically include digital meters, data loggers, and smart inverters that provide real-time information about voltage, current, and power output across your series string.
Key monitoring parameters include individual panel voltage levels, string current flow, and overall power production. Advanced systems often feature remote monitoring capabilities through smartphone apps or web portals, allowing you to track performance metrics from anywhere. These platforms typically display daily, monthly, and annual energy yields, helping you identify any efficiency drops or potential issues.
For series connections, voltage monitoring is particularly important as it helps detect potential issues like partial shading or panel degradation. Many systems incorporate automatic alert features that notify you when performance falls below expected levels or when maintenance might be required.
Integration with weather monitoring stations can provide valuable context by correlating energy production with environmental conditions. This data helps in understanding whether reduced output is due to natural factors or system issues. For optimal results, consider installing monitoring equipment that meets IEC 61724 standards, ensuring reliable and accurate performance assessment of your solar installation.
Safety and Maintenance Considerations
Regular safety inspections and proper maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of series-connected solar panels. Always disconnect the system before performing any maintenance work and wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including insulated gloves and safety glasses.
Check connection points quarterly for signs of corrosion or loose wiring, as these issues can significantly impact system efficiency and pose safety risks. During visual inspections, look for physical damage to panels, such as cracks or discoloration, which might indicate potential problems.
Keep panels clean from debris, dust, and bird droppings, particularly in dry regions. In European climates, snow removal during winter months is essential to maintain consistent power generation. However, avoid using harsh chemicals or abrasive materials that could damage the panel surface.
Monitor system performance regularly through your inverter display or monitoring system. Unexpected drops in power output might indicate connection issues in your series configuration. For safety-critical maintenance or electrical work, always engage certified solar professionals who understand local regulations and safety standards.
Maintain detailed records of all maintenance activities and system performance data to track long-term efficiency and identify potential issues early.
Connecting four solar panels in series presents an efficient solution for European property owners looking to optimize their solar energy systems. This configuration offers enhanced voltage output while maintaining consistent current flow, making it particularly suitable for residential and commercial installations where space optimization is crucial. As we’ve explored, proper installation techniques, regular maintenance, and adherence to safety guidelines are essential for maximizing system performance and longevity. With the continuous advancement of solar technology and Europe’s growing commitment to renewable energy, series-connected solar arrays will remain a cornerstone of sustainable power generation. Moving forward, innovations in smart monitoring systems and improved panel efficiency promise to make series connections even more effective and accessible for property owners across Europe. Remember to consult qualified professionals for your specific installation needs to ensure optimal performance and compliance with local regulations.
Leave a Reply