Off-Grid Hydro Power: The Missing Piece in Your Hybrid Energy System

Harness the untapped potential of flowing water to create reliable, renewable energy when designing your off-grid system. Micro-hydro power systems generate consistent electricity from streams and rivers, offering a dependable complement to solar installations across European landscapes. Unlike intermittent renewable sources, properly engineered hydro solutions deliver steady power output 24 hours a day, requiring just 2-3 meters of vertical drop and water flow rates of 20-30 liters per second for basic household needs.
This proven technology transforms modest water resources into sustainable energy independence, powering homes and businesses while adhering to EU environmental regulations. When integrated with modern battery storage and smart control systems, micro-hydro installations achieve remarkable efficiency rates above 70%, far exceeding most alternative renewable sources. The combination of hydro and solar creates a robust hybrid system that maximizes energy availability throughout seasonal variations, ensuring reliable power generation regardless of weather conditions or time of day.
Understanding Off-Grid Hydro Power Systems
Core Components of Micro-Hydro Systems
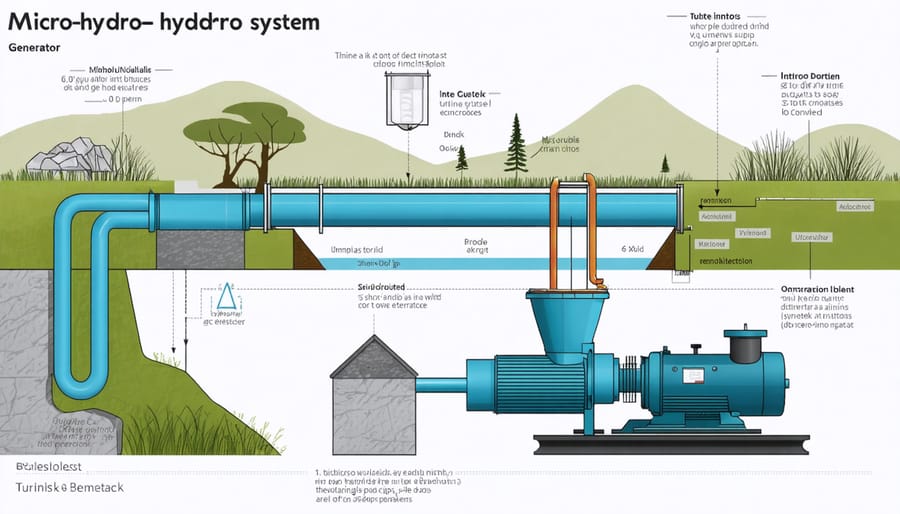
A micro-hydro system consists of three essential components that work together to transform flowing water into usable electricity. The heart of the system is the turbine, which converts the kinetic energy of moving water into mechanical energy through rotating blades. Different turbine types suit various water conditions: Pelton wheels excel with high heads and low flow rates, while crossflow turbines perform better with lower heads and higher flow rates.
Connected to the turbine, the generator transforms mechanical energy into electrical power. Most micro-hydro installations use either synchronous or induction generators, with synchronous types being particularly suitable for off-grid applications due to their self-exciting capabilities. The choice between single-phase and three-phase generators depends on your power requirements and intended usage.
The control system serves as the brain of the installation, managing power output and protecting the equipment. It includes essential components like load controllers, which maintain stable voltage and frequency by directing excess power to dump loads when necessary. Modern control systems often feature remote monitoring capabilities, allowing users to track performance and receive alerts about potential issues via smartphone applications.
Additional components include intake screens to filter debris, penstock pipes to channel water, and tailrace channels to return water to the stream. Together, these elements create a reliable, efficient system for generating clean electricity from flowing water.
Site Requirements and Assessment
Successful implementation of an off-grid hydro system begins with a thorough assessment of your site’s natural resources and physical characteristics. The two most critical factors are water flow rate and head height – the vertical distance water falls from intake to turbine. A minimum flow rate of 20 litres per second and a head height of at least 2 metres are typically required for viable power generation.
Your site’s location and accessibility also play crucial roles. Consider factors such as distance from the water source to your power consumption point, terrain characteristics, and seasonal variations in water flow. European regulations often require maintaining minimum environmental flows in streams, so year-round water availability assessment is essential.
A professional site survey will measure these parameters and evaluate additional factors like soil stability, flood risk, and environmental impact. This assessment should also consider local permits and water rights, which vary significantly across European regions. Many areas require environmental impact studies, particularly regarding fish populations and downstream water users.
The survey results will determine the optimal system size and type of turbine needed. While Pelton wheels work best with high heads and lower flows, crossflow turbines suit sites with lower heads and higher flows. Modern monitoring systems can help optimize performance by adjusting to seasonal variations in water flow.
Integration with Solar and Battery Systems

Balancing Power Sources
Creating an effective balance between hydro and solar power sources is crucial for maximizing the reliability of your off-grid system. When integrating renewable energy systems, understanding seasonal patterns becomes essential. Hydro power typically offers consistent output during wet seasons and winter months, while solar generation peaks during summer’s longer daylight hours.
The optimal mix depends on your location’s specific characteristics. In regions with year-round water flow, hydro power might constitute 60-70% of your system’s capacity, with solar serving as supplementary power. Conversely, in areas with seasonal streams, solar panels might need to provide the majority of power during dry periods.
To determine the right balance, conduct a detailed analysis of your site’s resources:
– Monitor water flow patterns across seasons
– Assess solar irradiance throughout the year
– Calculate your peak and baseline power requirements
– Consider battery storage capacity needs
Modern control systems can automatically manage the power distribution between sources, ensuring optimal efficiency. Installing a hybrid charge controller allows seamless switching between hydro and solar inputs while maintaining stable battery charging.
Remember that redundancy is key in off-grid systems. Even if your hydro resource is substantial, incorporating solar power provides valuable backup during maintenance periods or unexpected water flow disruptions. This dual-source approach also reduces wear on individual components by distributing the generation load, potentially extending system lifespan and improving overall reliability.
Energy Storage Solutions
Effective energy storage is crucial for maximising the potential of off-grid hydropower systems. Modern battery technologies, particularly lithium-ion solutions, work seamlessly with micro-hydro installations to ensure consistent power availability throughout the year. These storage systems bridge the gap during periods of lower water flow or increased energy demand.
The integration process typically involves a sophisticated power management system that coordinates between the hydro generator, battery bank, and household consumption. Advanced charge controllers monitor battery status and regulate charging cycles, protecting the batteries while optimising their lifespan. Most contemporary systems can store enough energy to power a typical European household for 2-3 days, providing essential backup during maintenance or unexpected system interruptions.
For optimal performance, battery systems should be sized according to your specific energy requirements and hydropower generation capacity. A well-designed storage solution typically includes:
– High-capacity lithium-ion or advanced lead-acid batteries
– Smart inverter systems for efficient AC/DC conversion
– Automated management systems for load balancing
– Temperature-controlled battery housing
– Remote monitoring capabilities
Regular maintenance and proper battery management can extend system life beyond 10 years, making it a cost-effective long-term investment. Modern storage solutions also feature smart grid compatibility, allowing for future expansion and integration with other renewable energy sources.
When designing your storage system, consider seasonal variations in water flow and energy consumption patterns. This ensures your system maintains reliability throughout the year while maximising the efficiency of your hydropower installation.
Implementation and Maintenance
Installation Best Practices
A successful off-grid hydro installation begins with a thorough site assessment. First, evaluate your water source’s flow rate and head (vertical drop) using professional measurement tools. These parameters will determine your system’s potential power output and guide equipment selection.
Next, obtain necessary permits and environmental clearances from local authorities. European regulations typically require detailed documentation regarding water usage and environmental impact assessments. Work with certified installers who understand regional compliance requirements.
The intake structure should be carefully positioned to minimize debris accumulation while ensuring consistent water flow. Install robust screening systems to protect turbine components from leaves and sediment. Proper pipeline sizing is crucial – oversizing reduces efficiency while undersizing restricts flow.
Ensure proper system grounding and implement comprehensive lightning protection measures, particularly important in mountainous regions. The powerhouse should be well-ventilated and secure, with adequate space for maintenance access.
Install monitoring systems to track performance metrics and detect potential issues early. Modern smart controllers can automatically adjust flow rates and load management for optimal efficiency. Consider incorporating a backup power source or storage system for periods of low water flow.
Finally, establish a maintenance schedule including regular intake cleaning, bearing lubrication, and electrical system checks. Document all installation parameters and operational procedures for future reference and troubleshooting.
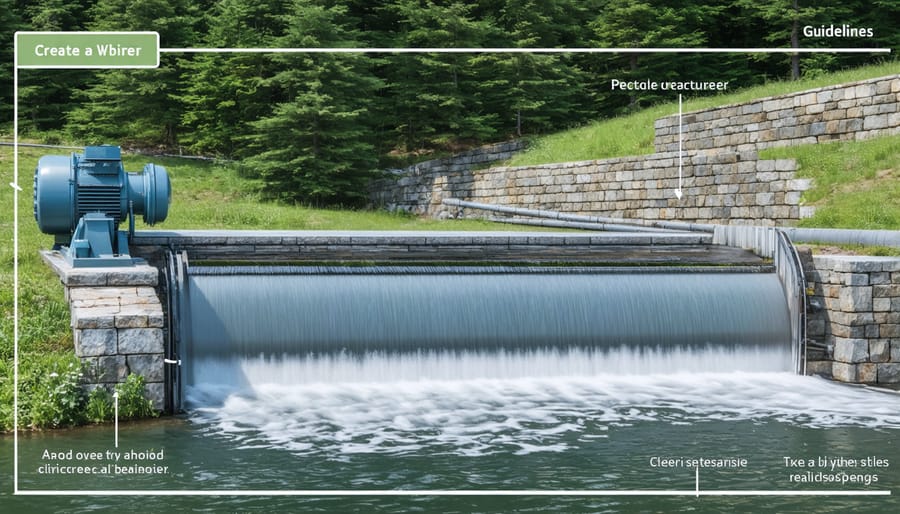

Maintenance Requirements
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the optimal performance and longevity of your off-grid hydro system. The most frequent tasks include inspecting and clearing debris from the intake screen, which should be done weekly or more often during autumn when leaves are falling. This simple action prevents system blockages and maintains consistent water flow.
Monthly maintenance involves checking all pipe connections for leaks, inspecting the turbine bearings for wear, and ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts. The penstock (water pipeline) should be walked and examined for any signs of damage or potential issues, particularly after severe weather events.
On a quarterly basis, conduct thorough electrical system checks, including battery connections, inverter performance, and controller settings. Pay special attention to water seals and gaskets, replacing them if any deterioration is noticed. The turbine housing should be inspected for sediment buildup, which needs to be cleaned to prevent efficiency losses.
Annual maintenance typically requires professional inspection of the entire system, including:
– Complete turbine disassembly and cleaning
– Bearing replacement if necessary
– Calibration of control systems
– Assessment of civil works (weir, intake, and tailrace)
– Testing of safety shutdown systems
For troubleshooting, maintain a log of system performance data to help identify any unusual patterns. Common issues like reduced power output often stem from intake blockages or bearing wear, while electrical problems typically relate to controller settings or battery maintenance.
Environmental and Regulatory Considerations
Installing an off-grid hydro system in Europe requires careful consideration of environmental factors and compliance with various regulatory requirements. Water rights and usage permissions are fundamental aspects that must be secured before project initiation. In most European countries, you’ll need to obtain permits from local water authorities and environmental agencies, particularly if your system affects natural waterways.
Environmental impact assessments are typically mandatory and evaluate factors such as fish migration patterns, sediment transport, and downstream water quality. Modern micro-hydro installations must incorporate fish-friendly features and maintain minimum ecological flow rates to protect aquatic ecosystems. These requirements vary by region and watershed characteristics.
Noise regulations also play a crucial role, especially in residential areas. While modern turbines are relatively quiet, sound-dampening measures may be necessary to meet local noise ordinances. Visual impact considerations are equally important, with some jurisdictions requiring screening or specific design modifications to preserve landscape aesthetics.
Water abstraction licenses are essential and usually specify maximum withdrawal rates and seasonal restrictions. Many European countries have implemented stricter regulations in recent years to ensure sustainable water management and protect biodiversity. Regular monitoring and reporting of water usage may be required as part of compliance procedures.
For systems integrated with existing infrastructure, additional permits relating to civil works and grid connection standby arrangements may be necessary. Local authorities typically require detailed technical documentation, including system specifications, installation plans, and safety measures.
It’s advisable to engage with environmental consultants familiar with local regulations early in the planning phase. This proactive approach helps identify potential challenges and ensures compliance with all necessary environmental standards while maximizing system efficiency and minimizing ecological impact.
Off-grid hydro power, when integrated into hybrid energy systems, presents a compelling solution for sustainable energy independence. The combination of hydroelectric power with other renewable sources, particularly solar, creates a robust and reliable energy infrastructure that can operate effectively throughout the year. European property owners and businesses implementing these systems benefit from reduced energy costs, enhanced grid independence, and a significantly lower carbon footprint.
The practical implementation of off-grid hydro requires careful consideration of several factors, including available water resources, terrain characteristics, and local regulations. When properly planned and executed, these systems can provide consistent baseline power generation that complements the intermittent nature of solar energy. This synergy is particularly valuable in regions with seasonal variations in sunshine and rainfall patterns.
Success in off-grid hydro implementation depends on thorough site assessment, professional system design, and regular maintenance. Property owners should work with experienced providers to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and optimize system performance. The initial investment, while significant, is offset by long-term energy cost savings and potential government incentives for renewable energy adoption.
Looking ahead, the integration of smart technology and energy management systems will further enhance the efficiency of hybrid hydro solutions. As European nations continue to prioritize sustainable energy transition, off-grid hydro systems represent a viable and environmentally responsible choice for those seeking energy independence while contributing to a greener future.
Leave a Reply