Legal Requirements for Off-Grid Solar: Essential Grounding Rules You Must Follow

Installing off-grid solar systems in Europe requires careful navigation of legal frameworks and safety regulations. While off-grid solar systems grounding remains a critical compliance requirement, the legality varies significantly across different European jurisdictions. Most EU member states permit off-grid installations, provided they meet local building codes, electrical safety standards, and environmental regulations. Property owners must secure proper permits, undergo professional inspections, and ensure installations comply with EN 62446 and IEC 60364 standards. Recent EU directives have actually simplified the process, recognizing off-grid solutions as vital contributors to energy independence and sustainability goals. Understanding these requirements early in the planning phase helps avoid costly modifications and ensures a smooth path to energy autonomy.
Legal Framework for Off-Grid Solar in Europe
National vs. EU Regulations
Off-grid solar installations in Europe are governed by both national and EU-level regulations, creating a multi-layered framework for compliance. At the EU level, key directives like the Renewable Energy Directive (RED II) establish overarching guidelines for renewable energy deployment, while individual member states maintain their specific requirements.
Most European countries require off-grid systems to meet safety standards outlined in the IEC 60364 electrical installation guidelines. However, local regulations can vary significantly. For instance, Germany mandates detailed documentation and professional installation certification, while France requires prior notification to local authorities for systems exceeding certain capacity thresholds.
In terms of building permits, Nordic countries typically have stricter requirements for off-grid installations due to extreme weather conditions, while Mediterranean nations often focus on aesthetic integration and heritage preservation. The EU’s Energy Performance of Buildings Directive (EPBD) influences national building codes, requiring consideration of renewable energy solutions in new constructions and major renovations.
For compliance, it’s essential to consult both national building authorities and local municipalities, as requirements can differ even between regions within the same country.
Required Permits and Documentation
While off-grid solar installations are legal across Europe, they typically require specific permits and documentation to ensure compliance with local regulations. Most municipalities require a building permit or planning permission before installation can begin. You’ll need to submit detailed system plans, including electrical diagrams, structural calculations, and site layouts.
Essential documentation usually includes proof of equipment certification (CE marking for European standards), warranty information, and manufacturer specifications. Many regions also require a professional assessment of your property’s solar potential and structural integrity.
For safety compliance, you’ll need documentation of proper grounding systems and electrical connections. Some areas mandate periodic safety inspections, requiring you to maintain inspection certificates and maintenance records.
It’s advisable to consult with local authorities early in the planning process, as requirements vary significantly between different European countries and even municipalities. Some regions offer streamlined permitting processes for residential solar installations, while others may require additional environmental impact assessments, especially in protected areas or historic districts.
Remember to retain copies of all permits and certifications for future reference and insurance purposes.

Essential Grounding Requirements
Equipment Grounding Standards
Proper equipment grounding is a crucial safety requirement for off-grid solar installations across Europe. The EU standards mandate that all metallic components of a solar power system must be connected to a common grounding point to prevent electrical hazards and ensure system reliability.
According to IEC 60364-7-712 standards, the grounding system must include the solar panel frames, mounting structures, and all metallic enclosures housing electrical components. The main grounding conductor should be properly sized according to system capacity, typically requiring a minimum of 6mm² copper conductor for residential installations and larger sizes for commercial systems.
Each array frame requires secure bonding to the grounding system using corrosion-resistant materials. The grounding electrode system must achieve a maximum resistance of 10 ohms, though local regulations may specify stricter requirements. Installation of surge protection devices (SPDs) is mandatory to protect against lightning strikes and voltage surges.
For battery storage systems, separate grounding considerations apply. The battery bank must be isolated from the solar array grounding system to prevent potential ground loops while maintaining safety standards.
Regular inspection and maintenance of grounding connections are essential, as environmental factors can lead to degradation over time. Documentation of the grounding system installation and subsequent inspections must be maintained to demonstrate compliance with local authorities and insurance requirements.
System Grounding Regulations
Proper system grounding is a critical safety requirement for off-grid solar installations across Europe. All off-grid systems must comply with IEC 60364-7-712 standards, which mandate specific grounding configurations to prevent electrical hazards and ensure system stability. Your solar installation requires two primary grounding elements: equipment grounding and system grounding.
Equipment grounding connects all metallic components of your solar system, including mounting frames, junction boxes, and inverter casings, to a common ground point. This protective measure prevents shock hazards by ensuring any fault current has a safe path to earth.
System grounding involves connecting one of the current-carrying conductors (typically the negative conductor in off-grid systems) to earth. This connection must be made through a properly sized grounding electrode system that meets local soil conditions and lightning protection requirements.
European regulations require periodic testing of grounding connections, with documentation maintained for compliance verification. The grounding resistance should not exceed 10 ohms in most cases, though specific requirements may vary by region and system size.
For safety and legal compliance, always engage certified professionals to design and install your grounding system. They will ensure proper conductor sizing, connection methods, and corrosion protection measures that align with both EU and local regulations.
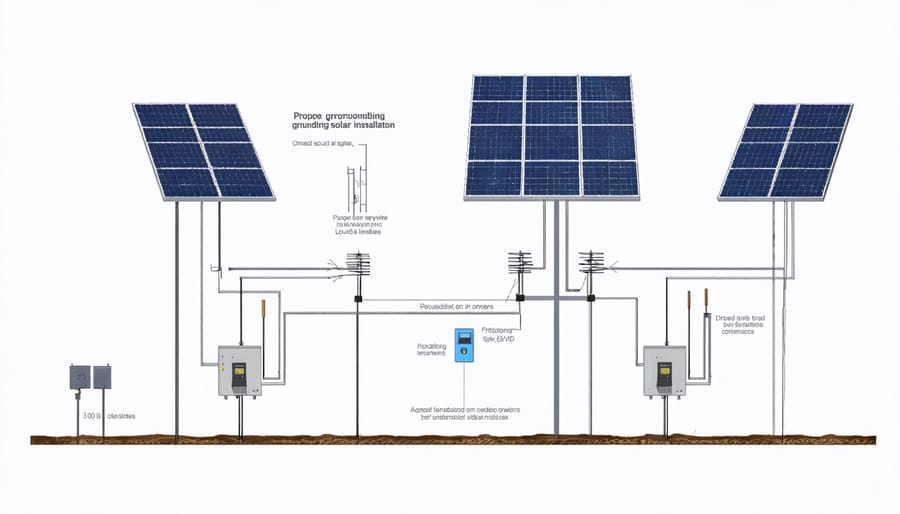
Safety Compliance and Inspections
Required Safety Features
When installing an off-grid solar system, several mandatory safety features must be in place to meet European regulations and ensure system reliability. The primary requirement is a proper grounding system that prevents electrical hazards and protects both equipment and users. This includes installing ground fault protection devices and surge protectors throughout the system.
Battery installations require ventilation systems and temperature controls to prevent overheating and gas accumulation, particularly for lead-acid batteries. Emergency disconnect switches must be readily accessible and clearly marked, allowing quick system shutdown in case of emergencies.
Charge controllers are mandatory to prevent battery overcharging and damage to system components. Additionally, proper circuit protection through appropriately sized fuses and circuit breakers is essential for preventing electrical fires and equipment damage.
All electrical connections must be housed in weatherproof enclosures that meet IP65 standards or higher, protecting against dust and water ingress. Warning signs and safety labels must be clearly displayed, indicating system voltage levels and potential hazards.
These safety features must be installed by certified professionals and regularly maintained to ensure continued compliance with European safety standards.

Inspection Procedures
Inspection procedures for off-grid solar installations vary across European regions, but generally follow a standardised process to ensure safety and compliance. Most jurisdictions require initial plan reviews, followed by multiple inspection phases during installation. The primary inspection typically occurs after mounting the solar panels but before final electrical connections, allowing inspectors to verify structural integrity and proper equipment placement.
A qualified electrical inspector will examine system components, including inverters, batteries, and safety disconnects. They’ll verify proper cable sizing, grounding methods, and protection against environmental factors. Documentation of component certifications and compliance with local building codes must be readily available during inspection.
Final approval usually requires demonstration of system functionality and safety features. Inspectors will verify proper labelling of components, emergency shutdown procedures, and the presence of required safety documentation. Some regions mandate periodic re-inspections, typically every 3-5 years, to ensure continued safe operation and compliance with evolving standards.
To facilitate smooth inspections, maintain detailed installation records and ensure all modifications are properly documented and approved by relevant authorities.
Professional Installation Requirements
Professional solar installation of off-grid systems requires certified expertise to ensure safety, compliance, and optimal performance. In the European Union, installers must possess specific certifications that vary by country, but generally align with the EU’s Renewable Energy Directive requirements.
Most member states require installers to hold national certifications or complete accredited training programmes. These qualifications typically cover technical competencies, safety protocols, and current regulations. Following professional solar installation guidelines is crucial for system longevity and insurance validity.
Key certification requirements often include:
– Electrical qualification certificates
– Specific solar PV installation training
– Health and safety certifications
– Regular updates on regulatory changes
While DIY installation might seem cost-effective, professional installation ensures:
– Proper system sizing and configuration
– Correct battery storage integration
– Compliant electrical connections
– Valid warranty protection
– Insurance coverage
– Meeting local building regulations
Professional installers also coordinate with local authorities for necessary permits and inspections, ensuring your off-grid system meets all legal requirements. They provide documentation proving compliance with relevant standards, which is essential for insurance and potential property resale.
Remember, improper installation can void equipment warranties, compromise safety, and result in significant legal complications. Investing in certified professional installation protects your investment and ensures peace of mind.
Installing off-grid solar systems in Europe is indeed legal, but success lies in careful adherence to local regulations and industry standards. Throughout this exploration, we’ve seen that while regulations vary across different European regions, the core requirements remain consistent: proper permits, professional installation, safety compliance, and adherence to local building codes.
The key to a legally compliant off-grid solar installation is thorough preparation and engagement with local authorities. This includes obtaining necessary permissions, ensuring proper documentation, and working with certified installers who understand both technical requirements and legal frameworks.
Remember that legal compliance isn’t just about ticking boxes – it’s about ensuring your system’s safety, efficiency, and longevity. By following proper procedures and maintaining open communication with relevant authorities, you can enjoy the benefits of sustainable energy independence while staying within legal boundaries.
As the renewable energy landscape continues to evolve, staying informed about current regulations and working with qualified professionals remains crucial for successful off-grid solar implementation. This approach not only ensures legal compliance but also contributes to Europe’s broader sustainability goals.
Leave a Reply