Install Your Own Solar Panels: A Proven Method That Saves Thousands

Installing your own solar panels can reduce energy costs by 40-60% while contributing to a sustainable future. This comprehensive installation overview guides you through the essential steps, from initial planning to final connection. With proper tools, safety equipment, and local permits, most homeowners can complete a solar installation within 2-3 weekends.
Before beginning, assess your roof’s structural integrity, calculate optimal panel placement for maximum sunlight exposure, and verify compliance with European energy regulations. Professional electrical certification remains mandatory for grid connection in most EU countries, but handling the mechanical installation yourself can save €3,000-5,000 on a typical 4kW system.
Success requires methodical planning, attention to safety protocols, and precise execution. This guide breaks down complex technical requirements into manageable steps while ensuring adherence to EU safety standards and building codes. Whether you’re an experienced DIY enthusiast or technically inclined homeowner, solar panel installation represents a rewarding project with significant long-term benefits.
Essential Safety Considerations and Prerequisites
Required Permits and Regulations
Before starting your DIY solar panel installation, you must obtain the necessary permits and comply with local regulations. In most European countries, you’ll need a building permit or specific solar installation permit from your local authority. Contact your municipality’s building department to understand the specific requirements for your area.
Key documentation typically includes electrical permits, structural engineering certificates, and grid connection applications. Many European countries require certification from a qualified electrician for the final grid connection, even for DIY installations. You’ll also need to notify your energy provider about the planned installation and arrange for a bi-directional meter installation.
Check if your property falls under any heritage protection or conservation area restrictions, as these may affect your installation plans. Some regions have specific requirements regarding panel placement, maximum system size, and aesthetic guidelines. Additionally, ensure your installation complies with EU energy efficiency standards and local building codes.
Remember to document all permits and keep copies of approved applications. This documentation is essential for insurance purposes and may be required for claiming renewable energy incentives or tax benefits.
Safety Equipment and Tools
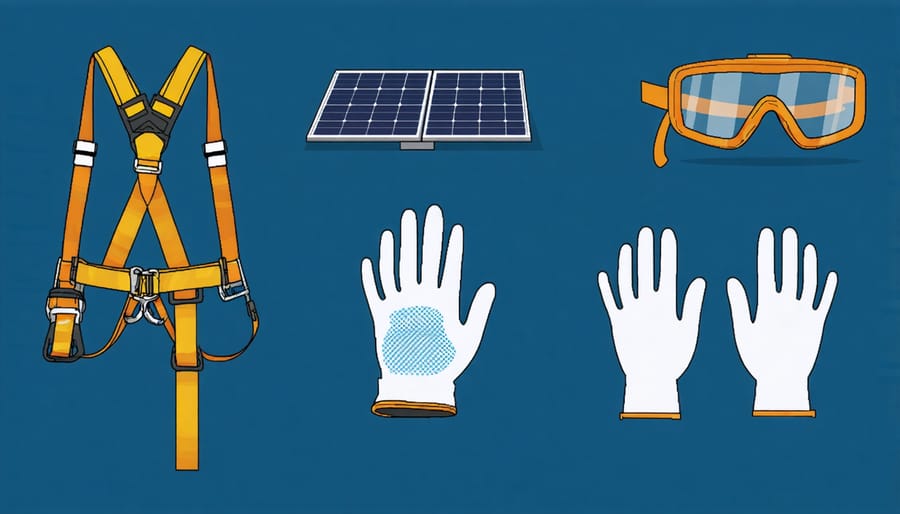
Before beginning your solar panel installation, ensure you have all necessary safety equipment and tools. Essential safety gear includes a sturdy safety harness with proper anchoring points, non-slip work boots, heavy-duty work gloves, and protective eyewear. A hard hat is crucial for protection against falling objects, while high-visibility clothing enhances safety during rooftop work.
For the installation itself, you’ll need basic tools such as a power drill with various bits, measuring tape, pencil, and level. Specialist equipment includes MC4 connector tools, solar cable cutters, and a voltage meter for testing. A battery-powered impact driver will make mounting brackets easier, while rope and pulleys help safely lift panels to the roof.
Keep weatherproofing materials ready: silicone sealant, flashing, and appropriate screws for your roof type. Don’t forget a sturdy ladder rated for your weight plus equipment. Having a tool belt or bucket will keep everything organised and easily accessible while working at height.
Remember to inspect all safety equipment before use and never work alone during installation. Keep a first-aid kit nearby and ensure your mobile phone is fully charged for emergencies.
Planning Your Solar Installation
Site Assessment and Roof Evaluation
Before installing solar panels, a thorough evaluation of your roof’s condition and orientation is crucial for optimal system performance. Begin by following established roof assessment guidelines to verify structural integrity and load-bearing capacity. Check for signs of damage, worn shingles, or necessary repairs that should be addressed before installation.
The ideal roof orientation for European installations is south-facing, though southeast and southwest orientations can also yield good results. Your roof’s pitch should typically be between 30-45 degrees for maximum solar exposure, though this may vary based on your specific location within Europe. Use a compass or digital tool to determine your roof’s exact orientation and measure the angle accurately.
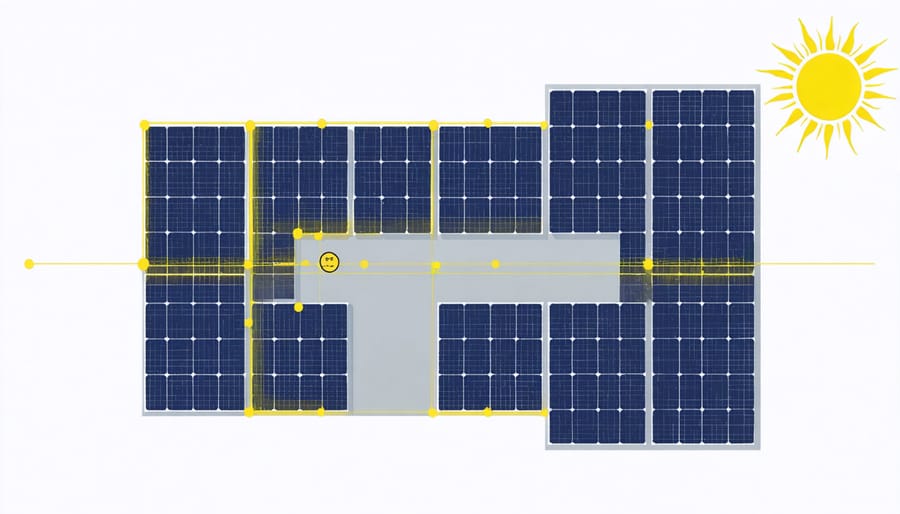
Assess available roof space, accounting for obstructions like chimneys, vents, and satellite dishes. Consider shadows cast by nearby buildings, trees, or other structures throughout the day and seasons. A solar pathfinder tool can help identify potential shading issues that might affect panel efficiency.
Document your roof’s measurements, including length, width, and usable area. Calculate the number of panels that can fit safely while maintaining appropriate spacing for maintenance access and adhering to local building regulations. Remember to factor in setback requirements from roof edges and fire safety zones as specified by European standards.
System Sizing and Component Selection
Proper system sizing begins with a detailed assessment of your household’s energy consumption. Review your electricity bills from the past 12 months to determine your average daily usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh). For European homes, typical consumption ranges from 2,500 to 5,000 kWh annually, though this varies by region and lifestyle.
To calculate your required system size, divide your daily energy consumption by the average peak sun hours in your location. For example, if you use 20 kWh per day and have 4 peak sun hours, you’ll need a system rated at approximately 5 kW. Remember to factor in system losses, which typically range from 15-25%.
When selecting components, focus on three main elements: solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems. Choose solar panels based on efficiency ratings and warranty periods, with premium European panels typically offering 20-25 year warranties. Monocrystalline panels are often preferred for residential installations due to their higher efficiency and smaller footprint.
For inverters, consider whether string inverters or microinverters better suit your needs. String inverters are more cost-effective but less optimal for partially shaded installations. Your mounting system should match your roof type and local wind load requirements, with adjustable mounting rails providing flexibility during installation.
Don’t forget to include safety equipment like DC isolators and surge protection devices, which are mandatory in most European countries. Calculate additional space for future system expansion, typically 20-30% extra capacity.
Creating Your Installation Plan
Creating a solid installation plan is crucial for a successful DIY solar panel project. Begin by assessing your roof’s orientation and angle – south-facing roofs with a 30-45 degree pitch are ideal for European latitudes. Consider potential shading from nearby trees, buildings, or chimneys that could affect solar panel performance throughout the day.
Next, calculate your energy requirements by reviewing your electricity bills from the past 12 months. This helps determine the number and size of panels needed. Remember to account for seasonal variations in energy consumption and solar production.
Develop a detailed layout design by measuring your available roof space. Allow for maintenance access and respect local building regulations regarding setbacks from roof edges. A typical residential system requires approximately 20-25 square meters for a 4kW installation.
Document your mounting strategy based on your roof type. Whether you have concrete tiles, slate, or metal roofing will influence the mounting hardware needed. Create a wiring diagram showing how panels will connect to the inverter and your home’s electrical system.
Finally, compile a comprehensive materials list including panels, inverter, mounting hardware, cables, and safety equipment. Check that all components meet European safety standards and certification requirements. Consider factors like wind load calculations and snow load capacity, particularly important in northern European regions.
Remember to obtain necessary permits and ensure your installation plan complies with local building codes and electrical regulations before proceeding with the installation.
Step-by-Step Installation Process
Mounting System Installation
The foundation of a successful solar panel installation lies in properly securing your mounting system. Before beginning, spend time choosing the right mounting materials for your specific roof type and local weather conditions. Most European residential installations use aluminum rails with stainless steel hardware for optimal durability and corrosion resistance.
Start by marking your roof attachment points according to your layout plan, ensuring they align with roof rafters or trusses. Using a chalk line, create precise guidelines for mounting rail placement. Install roof attachments by pre-drilling pilot holes and securing them with appropriate flashing to maintain water-tight roof integrity. Apply weatherproof sealant around each mounting point to prevent water ingress.
Attach the mounting rails to your roof brackets, ensuring they’re perfectly level using a spirit level. Most systems use a combination of mid and end clamps – position these according to manufacturer specifications. Maintain consistent spacing between rails as specified in your mounting system manual, typically 1.2 to 1.6 meters apart.
For maximum stability, install additional rail supports at areas of high stress, such as edges and corners. Double-check all bolts are tightened to the recommended torque specifications, but avoid over-tightening which could damage components. Remember to leave adequate spacing between rail sections for thermal expansion, particularly important in European climates with significant temperature variations.
Verify all mounting components are securely fastened and properly aligned before proceeding with panel installation. This foundation will support your solar array for decades to come, so attention to detail at this stage is crucial for long-term system reliability.

Panel Placement and Securing
With your mounting rails secured, it’s time for the crucial step of placing and securing your solar panels. Begin by carefully lifting each panel onto the rails – this is definitely a two-person job for safety. Ensure you’re following your specific solar panel frame installation guidelines, as different manufacturers may have varying requirements.
Position each panel with approximately 2-3 cm gaps between them to allow for thermal expansion. Align the first panel at the edge of your mounting rails, ensuring it’s perfectly square with your roof line. This initial placement is critical as it sets the alignment for all subsequent panels.
Secure the panels using the provided mid and end clamps. Start with end clamps on the outer edge of your first panel, tightening them to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications. As you add subsequent panels, use mid clamps between them to create a secure, unified array. These clamps typically slide into the mounting rails and grip the panel frames firmly when tightened.
Check each panel’s stability by gently testing the mounting points. There should be no movement or wiggle room once properly secured. Pay special attention to edge panels, which may experience more wind load. For additional security in high-wind areas, consider installing supplementary mounting points as per local building regulations.
Remember to keep your panels clean during installation and avoid stepping on them at any point. Once all panels are secured, double-check all mounting hardware and ensure all electrical connections remain accessible for the wiring phase.
Electrical Wiring and Connections
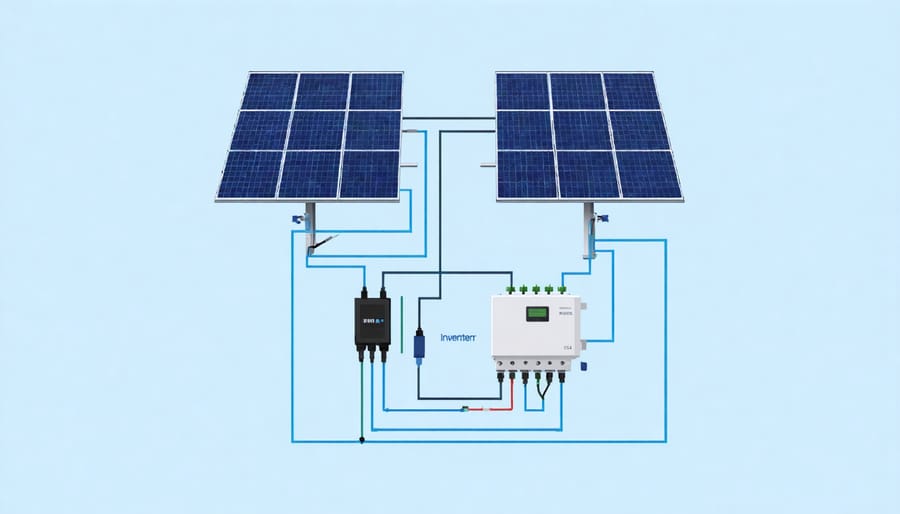
The electrical wiring phase requires careful attention to detail and strict adherence to safety protocols. Begin by connecting your solar panels in series or parallel, depending on your system design and inverter specifications. For series connections, link the positive terminal of one panel to the negative terminal of the next, while parallel connections require linking all positive terminals together and all negative terminals together.
Use appropriate MC4 connectors and solar-rated cables (minimum 4mm² cross-section for residential installations) to ensure safe, weather-resistant connections. When routing cables, maintain proper spacing and use UV-resistant cable ties or conduits to protect wiring from environmental damage. Pay special attention to proper system grounding to ensure safety and compliance with European electrical codes.
Install a DC isolation switch between the solar array and inverter, ensuring it’s readily accessible for maintenance and emergency shutdown. Connect the inverter to your home’s electrical system through an AC isolation switch and appropriate circuit breakers. All connections should be made within junction boxes rated for outdoor use (minimum IP65 rating in European installations).
Remember to double-check all connections before finalizing the installation. Use a multimeter to verify proper voltage levels and polarity. Label all cables and switches clearly according to European standards, indicating circuit information and shutdown procedures. This attention to detail in your electrical work will ensure a safe, efficient, and compliant solar installation that meets all local regulations.
Inverter Installation and System Testing
The inverter installation represents a crucial phase in your solar panel system setup, as it converts the DC power generated by your panels into usable AC power for your home. Begin by selecting a cool, dry, and easily accessible location for your inverter, preferably near your main electrical panel while staying within manufacturer-specified cable length limits.
Mount the inverter on a solid wall using appropriate brackets and fixtures, ensuring it’s perfectly level and at a comfortable height for maintenance. Remember to maintain adequate clearance around the unit for proper ventilation – typically 30cm on all sides. Connect the DC cables from your solar panels to the inverter’s input terminals, carefully matching positive and negative connections while following your region’s polarity colour codes.
For the AC side, engage a certified electrician to connect the inverter to your home’s electrical system through an appropriate circuit breaker. This step is mandatory in most European countries and ensures compliance with local electrical regulations.
Before activating the system, perform these essential tests:
– Verify all electrical connections are tight and properly insulated
– Check DC voltage levels from the solar array
– Confirm proper grounding connections
– Ensure all safety switches are correctly installed
Once these checks are complete, power up the system gradually: first the DC isolator, then the AC circuit breaker. Your inverter’s display should show startup information and begin monitoring power production. Modern inverters often include WiFi connectivity – configure this to track your system’s performance through the manufacturer’s monitoring platform.
Wait for a clear, sunny day to conduct final performance testing and verify that power output aligns with your system’s specifications.
Final Inspection and Activation
Professional Inspection Requirements
Professional inspections are a crucial requirement for DIY solar installations across Europe, ensuring both safety and compliance with local regulations. Most jurisdictions require at least two mandatory inspections: one after mounting the racking system but before panel installation, and another final inspection once the entire system is complete.
Your local building authority will need to verify proper structural attachment and weatherproofing of roof penetrations during the initial inspection. The final inspection typically covers electrical connections, grounding systems, and overall installation quality. In many European countries, you’ll need to arrange for a certified electrician to inspect and approve all electrical work before grid connection is permitted.
Documentation requirements vary by region, but typically include electrical diagrams, structural calculations, and equipment specifications. It’s essential to schedule these inspections well in advance to avoid project delays. Some authorities may also require periodic safety inspections after installation, particularly for systems exceeding certain size thresholds.
Keep detailed records of all inspections and maintain contact with your local building department throughout the project to ensure compliance with current standards.
Grid Connection and System Activation
The final phase of your solar installation involves connecting your system to the grid and obtaining necessary approvals. First, contact your local Distribution Network Operator (DNO) to notify them of your installation and schedule a connection assessment. They’ll verify that your system meets all regional safety standards and grid compatibility requirements.
Ensure you have a certified electrician perform the final grid connection. They’ll install the proper isolation switches, configure your inverter settings according to local grid codes, and establish the monitoring system. The electrician will also conduct comprehensive testing of all safety mechanisms and verify proper system grounding.
Once the physical connection is complete, you’ll need to register your installation with relevant authorities and energy providers. In most European countries, this involves submitting documentation to receive your feed-in tariff registration and generation meter installation. Your local energy provider will then install a bi-directional meter that tracks both energy consumption and production.
After receiving final approval, your installer or electrician will guide you through system activation and basic operational procedures. Keep all documentation, including warranties and maintenance schedules, in a safe place for future reference.
Installing solar panels yourself is a rewarding project that can significantly reduce your energy costs while contributing to a sustainable future. By following proper planning procedures, securing necessary permits, and adhering to European safety standards, you can successfully complete your solar installation. Remember to thoroughly assess your roof’s condition, calculate your energy needs, and invest in quality components before beginning. While DIY installation can save money, don’t hesitate to consult professionals for complex electrical connections or when in doubt about safety requirements. With your system installed, you’ll be ready to enjoy clean, renewable energy while increasing your property’s value. Consider scheduling regular maintenance checks to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your solar investment. The transition to solar power is a significant step toward energy independence and environmental stewardship.
Leave a Reply