How Renewable Microgrids are Revolutionizing Europe’s Energy Landscape

Elevate your energy strategy by integrating renewable microgrids, tailored for European landscapes. Harness solar power by conducting a comprehensive site assessment, focusing on sunlight exposure and roof orientation, to maximize energy capture. Streamline operations by pairing cutting-edge battery storage solutions with your microgrid, ensuring resilience during peak demand or grid outages. Collaborate with local policymakers and grid operators to navigate regulations and secure necessary approvals, fostering a seamless integration process. Leverage the expertise of leaders like INOX Solar to customize scalable solutions that optimize efficiency and sustainability, transforming your energy system into a robust, future-proof asset.
Understanding Renewable Microgrids
Key Components of a Microgrid
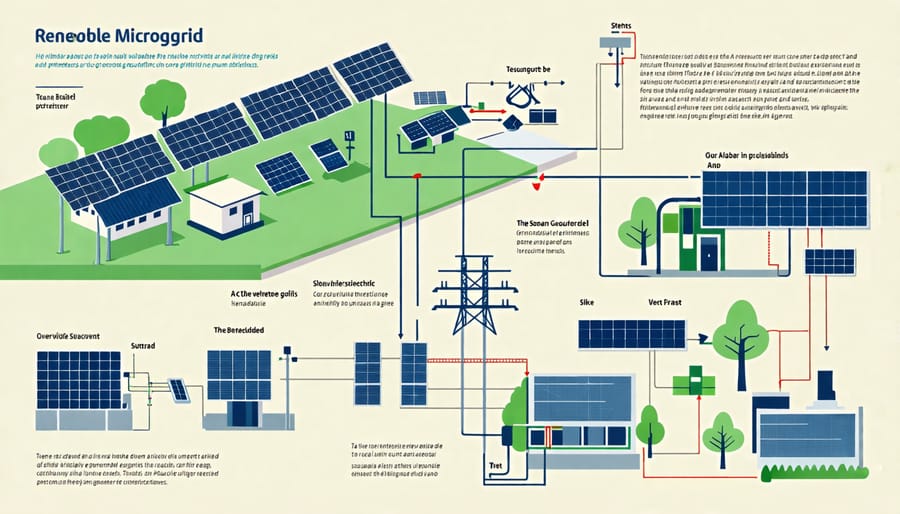
A microgrid is a localized power system that can operate independently or in conjunction with the main electrical grid, offering increased energy security and sustainability. At its core, a renewable microgrid typically includes several key components. Solar panels are often the primary source of electricity, capturing sunlight and converting it into energy. For European homeowners and businesses interested in harnessing solar energy, learning how to install solar panels is a crucial step toward energy independence.
Complementing solar panels, batteries serve as storage solutions, ensuring that excess solar power is stored efficiently for use during non-sunny periods, enhancing energy reliability. Control systems, the third vital component, are the intelligent platforms that manage the energy flow within the microgrid, optimizing efficiency and ensuring seamless transitions between grid modes. Together, these components embody innovation and sustainability, promising a reliable energy future tailored to European needs while supporting broader ecological and energy efficiency goals.
Differences from Traditional Grids
Renewable microgrids diverge significantly from traditional centralized power grids in their operational approach and energy sources. Unlike conventional systems that depend on large-scale power plants and extensive transmission networks, microgrids operate with greater autonomy, often managing localized energy production and consumption. This autonomy is pivotal in integrating renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, allowing for improved efficiency and reliability. In Europe, where sustainability and innovation are highly prioritized, microgrids enable homeowners, businesses, and industries to not only reduce carbon footprints but also enhance energy security and resilience. Embracing technology and adaptability, microgrids offer comprehensive support for achieving sustainable energy goals.
Benefits of Renewable Microgrids
Environmental and Economic Impact
Renewable microgrids represent a transformative approach to energy management, substantially impacting both environmental sustainability and economic efficiency. By incorporating renewable energy sources such as solar power, these microgrids significantly reduce carbon emissions, aiding European efforts to combat climate change. Their localized nature minimizes dependency on large-scale power plants, which further decreases environmental footprint and enhances energy resilience during grid disruptions.
Economically, renewable microgrids offer a pathway to cost efficiency for European homeowners, businesses, and industries. Initial investments in microgrid infrastructure are offset by long-term savings on energy bills, driven by reduced reliance on traditional, often volatile energy markets. Businesses can benefit from increased energy independence, protecting themselves from price fluctuations and supply interruptions.
Moreover, the adoption of renewable microgrids fosters innovation and job creation within the clean energy sector, providing a boost to local and national economies. Comprehensive support for these projects ensures that stakeholders are equipped with the necessary knowledge and tools, reinforcing Europe’s commitment to sustainable energy solutions and a greener future.

Energy Independence and Security
Renewable microgrids significantly bolster energy independence and security, essential for the sustainable future of Europe’s energy landscape. By decentralizing electricity generation, these microgrids allow homeowners, businesses, and industries to produce their own energy, primarily through solar power. This local generation reduces reliance on traditional, centralized power grids, thus mitigating risks associated with grid failures or blackouts. Moreover, microgrids enhance energy efficiency by minimizing transmission losses and providing a reliable, resilient framework tailor-made for European climatic conditions.
The innovative use of renewable sources within microgrids offers adaptable solutions to energy challenges, ensuring stable supply even amidst fluctuating demands. This autonomy appeals to various stakeholders who seek comprehensive project support for integrating advanced energy solutions into their operations. As a catalyst for sustainable development, microgrids not only foster energy independence but also position Europe at the forefront of the global transition towards cleaner energy alternatives, reinforcing both regional security and environmental stewardship.
Challenges in Implementing Microgrids
Technical and Financial Hurdles
Implementing renewable microgrids presents both technical and financial challenges that stakeholders must carefully navigate. Technically, the integration of microgrids with existing energy infrastructure requires advanced control systems and sophisticated software to ensure seamless operation, particularly in balancing supply and demand. This complexity is compounded when deploying diverse energy sources like solar and wind, necessitating reliable energy storage solutions to manage variability and maintain a consistent power supply. In the European context, interoperability within diverse regulatory landscapes adds further complexity, demanding innovative approaches tailored to specific regional needs.
Financially, the initial capital investment for renewable microgrid projects can be considerable. Businesses and communities often face difficulties in securing funding and achieving attractive returns on investment. The absence of standardized incentive structures across the European continent poses additional financial risks. However, as innovations drive down costs and nations emphasize sustainability goals, financial barriers are increasingly being addressed through comprehensive project support and collaborative funding models. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for stakeholders eager to embrace the efficiencies and sustainability offered by renewable microgrids.
Policy and Regulatory Considerations
Policy and regulation play a crucial role in the adoption of renewable microgrids, as they can either facilitate or hinder progress. In Europe, forward-thinking policies are pivotal in driving innovation and sustainability by providing incentives and subsidies for renewable energy solutions. National and regional regulations often determine the feasibility of microgrid projects, impacting everything from grid access to financial viability. The European Union’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions underlines the importance of supportive regulatory frameworks, promoting efficiency and adoption across industries, businesses, and homes. Emphasizing comprehensive project support, these frameworks are essential for overcoming challenges and ensuring a sustainable energy future.
European Success Stories
Case Study: Germany’s Renewable Transition
Germany has emerged as a global frontrunner in renewable energy adoption, particularly in the implementation of renewable microgrids. By integrating solar energy with state-of-the-art microgrid systems, Germany demonstrates a commitment to sustainability and innovation. These microgrids ensure efficiency and reliability, enabling communities and industries to generate, store, and distribute electricity independently. The German transition showcases the profound impact of comprehensive project support, enabling nationwide scalability and resilience in energy supply. This successful transformation offers valuable insights for European homeowners and businesses eager to embrace sustainable solutions. By reducing dependency on fossil fuels and enhancing energy security, Germany’s strategic approach underlines the potential of renewable microgrids to revolutionize the energy landscape across Europe, guiding the continent toward a sustainable future.
Case Study: Microgrid Projects in Nordic Countries
In the Nordic countries, microgrid projects are making remarkable strides in advancing sustainable energy goals. These projects, often harnessing the region’s abundant renewable resources such as wind, solar, and hydropower, are not only reducing carbon footprints but also enhancing energy efficiency and resilience. For instance, Sweden’s Åland Islands project integrates multiple renewable energy sources, demonstrating how microgrids can effectively meet community energy needs while ensuring stability and sustainability. Finland’s LEMENE project underscores innovation, enabling energy self-sufficiency in industrial areas through a seamless mix of renewables and backup power. Such initiatives reflect a broader European impact, showcasing how comprehensive support and collaboration among governments, industry players, and local communities can drive forward the renewable energy transition. These projects offer valuable insights and models for other regions aiming to achieve similar sustainability milestones.
The Future of Renewable Microgrids in Europe
Technological Innovations on the Horizon
As renewable microgrids advance, exciting technological innovations are on the horizon. One notable development is the integration of smart control systems, enhancing grid efficiency and reliability through real-time data analysis. Additionally, advancements in energy storage, particularly in battery technologies, promise to improve the stability and sustainability of these grids. In Europe, these innovations are essential as nations strive for energy independence and push toward a greener future. Furthermore, the advent of decentralized energy markets could transform how solar energy solutions are adopted, offering European homeowners and businesses unprecedented control over their energy usage. With comprehensive support for projects ranging from individual homes to large industries, these solar panel innovations are set to redefine how we power our world.
INOX Solar’s Role in Shaping the Future
INOX Solar is at the forefront of developing renewable microgrids across Europe, driving innovation and sustainability in the energy sector. With its cutting-edge battery innovations, the company is enhancing the efficiency and reliability of solar energy solutions, making them more accessible for homeowners and businesses alike. INOX Solar supports every stage of renewable microgrid projects—from design to implementation—ensuring comprehensive and tailored solutions for its clients. Their commitment to sustainability and technological advancement is not only shaping the future of energy in Europe but also empowering communities to embrace cleaner, more efficient energy sources. As the demand for renewable energy systems grows, INOX Solar’s expertise and strategic approach position it as a pivotal player in advancing Europe’s microgrid infrastructure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, renewable microgrids are pivotal in advancing Europe’s energy independence and sustainability goals. They offer a resilient and efficient solution to the challenges of conventional energy infrastructures, enabling communities and industries to generate and manage their own clean energy. Companies like INOX Solar are at the forefront of this transformation, delivering comprehensive support for solar energy projects across Europe. Their innovation and expertise not only bolster local economies but also contribute significantly to reducing carbon footprints. As Europe moves towards a greener future, embracing these technologies is essential for ensuring a stable and sustainable energy landscape for generations to come.
Leave a Reply